The most successful newcomers to the market entry strategy are those who provide cutting-edge goods with superior craftsmanship and contemporary styles. Innovative high-tech American goods, including software, electronic components, healthcare and medical devices, synthetic materials, automotive technology, and information technology, are well received by Germans. Germany has a slightly above-average rate of high-speed internet connectivity for businesses, despite having an above-average rate for private households in the EU. For American producers, some agricultural products provide promising export opportunities. For German shoppers, price is a crucial consideration, but it’s not always the only one; in most cases, it’s more about “value for money.”

Interests and preferences vary from region to region in the fragmented and heterogeneous German market. In order to have a strong national market presence, successful marketing strategies take regional variances into account. Given that domestic companies with established presences are the main competitors for the majority of American products, experienced representation is a significant advantage to any market strategy. By providing premium goods and services at affordable costs together with locally sourced post-purchase assistance, American businesses may overcome this fierce competition. Although deductions, credits, and write-offs help to bring effective tax rates down to levels that are competitive worldwide, Germany’s relatively high marginal tax rates and complex tax regulations may be a barrier for investors.
A Market Entry Strategy: What Is It?
A significant endeavor, entering a new market can increase the influence, income, and reach of your business. A well-defined market entry plan acts as a road map for how you will present your goods or services to a new market, deal with regional circumstances, and get over potential roadblocks.
Establishing a Strategy for Entering a Market
The procedures, materials, and techniques you will employ to enter a new market are described in a market entry strategy. It directs choices on marketing, distribution, pricing, and product attributes. Your approach should be tailored to the particular requirements of the market, whether you intend to launch a new category of offerings domestically or plan a product market entry into a foreign country.
Creating a new market entry plan requires thorough study to comprehend local laws, competitor advantages, and consumer behavior. The ultimate objective is to provide a strong foundation for your company, ensuring that you speak to the appropriate audiences and communicate clearly.
The Importance of Market Entry for Long-Term Development
A market entrance and growth plan addresses both how to get into a market and how to expand once you’re there. You provide the groundwork for scaling up, investigating nearby markets, or growing your product lines by making plans in advance. This proactive strategy guarantees that your initial efforts result in continued success.
Key Techniques for Entering the Market
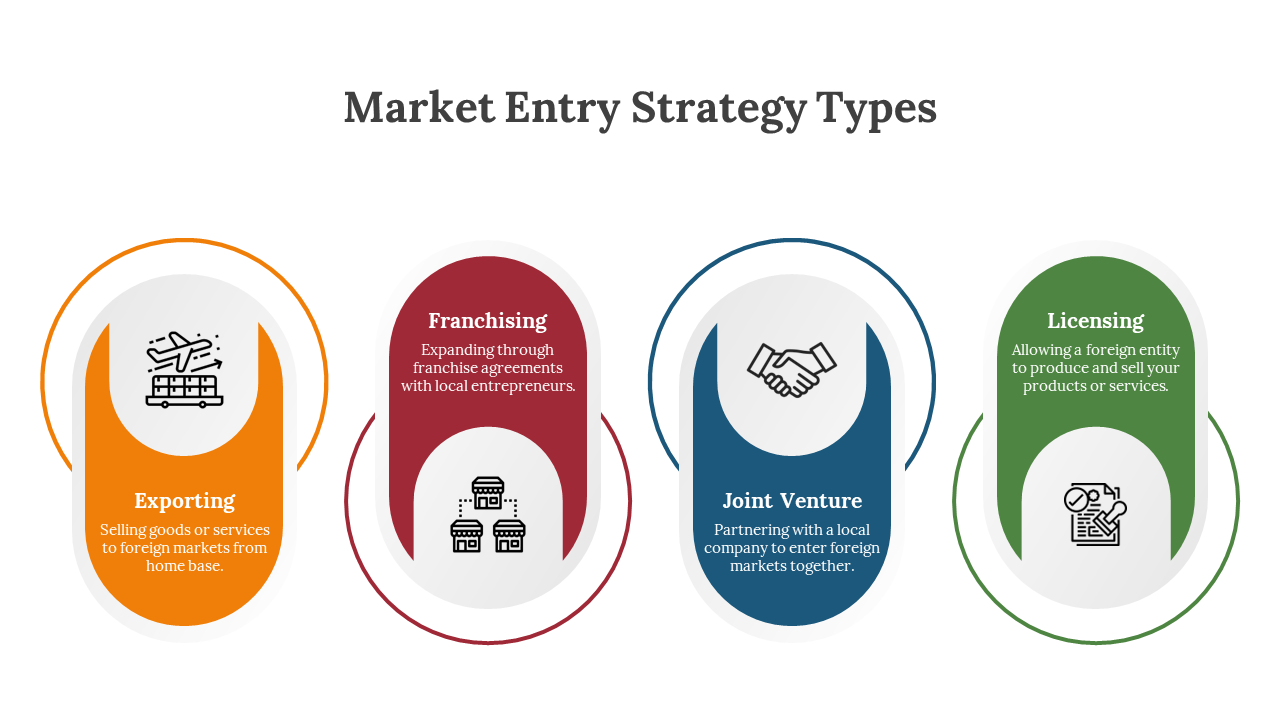
There are numerous approaches to market entry to take into account. Your objectives, available resources, and the target market’s complexity will all influence your decision. Typical methods include:
exporting. Selling products into a new market from your home base is known as exporting.
licensing. Giving a local company permission to manufacture or market your product on certain terms is known as
franchising. Giving a franchisee permission to utilize your model and brand is known as
Joint ventures: Associating with a nearby business to exchange resources and expertise.
“direct investment.” Establishing your own presence by putting up offices or facilities is known as “

Developing a Novel Approach to Market Entry
Take into account the following actions when developing a new market entry strategy:
Market research: Compile information about rivals, market size, and consumer behavior.
Define your target audience by figuring out who your ideal clients are and what they require.
Product Adaptation: Modify services, packaging, or product attributes to accommodate regional preferences.
Pricing and Promotion: Develop marketing strategies that engage consumers and set pricing that is competitive with the local market.
Distribution Strategy: To efficiently reach clients, select trustworthy partners and distribution channels.
Continuous Improvement: Track outcomes, get input, and gradually improve your approach.