🔹1.Definition Embedded Systems Development
A computer Embedded Systems Development created to carry out a particular task inside a broader mechanical or electrical system—often with real-time computing constraints—is known as an Embedded Systems Development.
🔹2. Core Components
1.Hardware
- Microcontroller / Microprocessor about development (e.g., ARM, AVR, PIC)
- Memory (RAM, ROM, Flash)
- I/O interfaces (GPIO, ADC, UART, SPI, I2C)
- Sensors & Actuators
2.Software
- Firmware (written in C/C++ or Assembly)
- Operating System (if used) — RTOS, Linux, or bare-metal
- Device drivers and middleware
🔹 3. Development Process
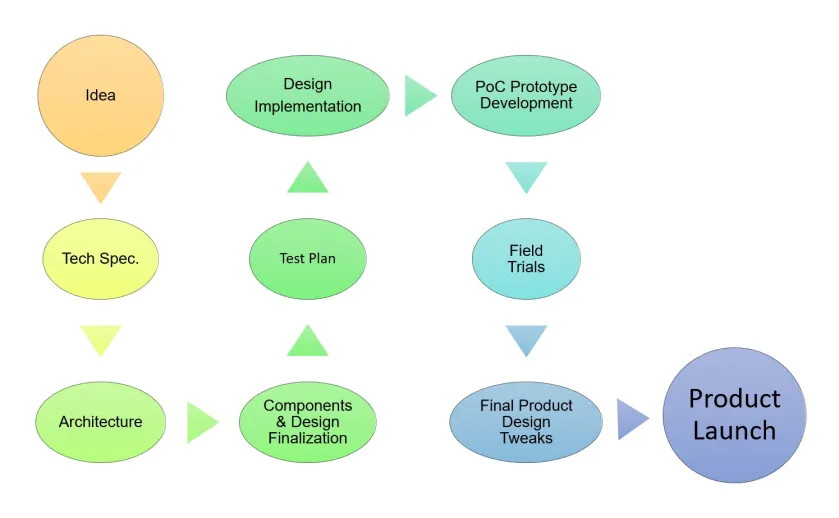
- Requirement Analysis – Define the purpose and constraints.
- System Design – Choose hardware and architecture.
- Implementation – Write and test Embedded Systems Development
- Integration & Testing – Hardware-software testing.
- Deployment & Maintenance – Optimize performance and reliability.
🔹 4. Programming Languages
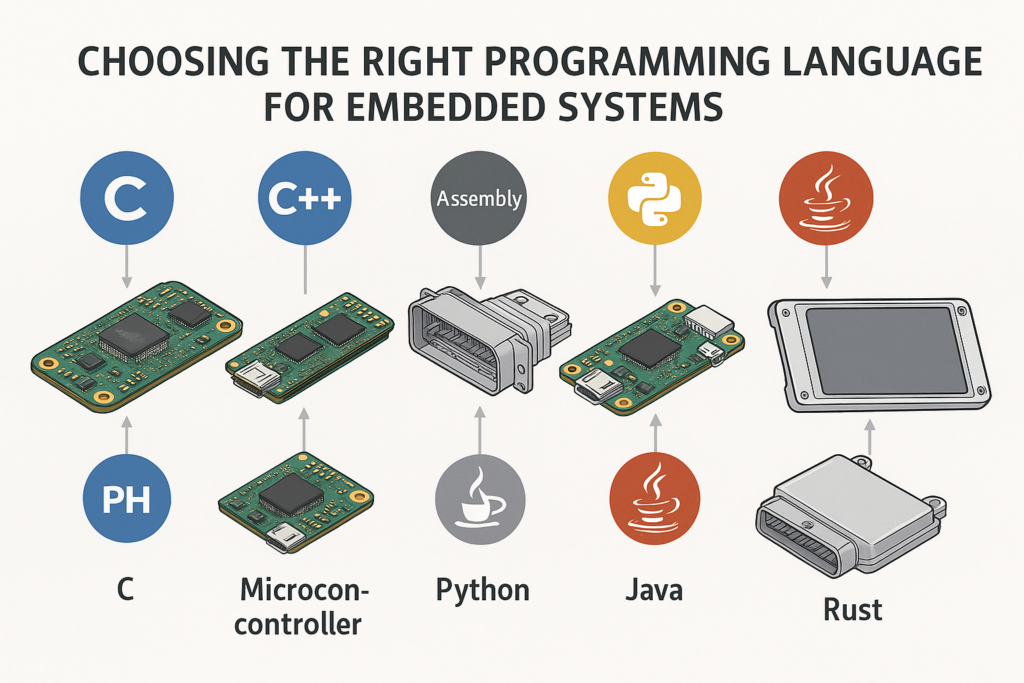
- C (most common)
- C++
- Assembly
- Python (for prototyping)
- Embedded Rust / Ada (for safety-critical systems)
🔹 5. Tools
- IDE: Keil, MPLAB, STM32CubeIDE, Arduino IDE
- Compilers: GCC, IAR, ARM Compiler
- Debuggers: JTAG, SWD, Logic Analyzer
- Simulators: Proteus, QEMU
🔹 6. Key Features
- Real-time operation
- Low power consumption
- Compact size
- High reliability
- Dedicated functionality
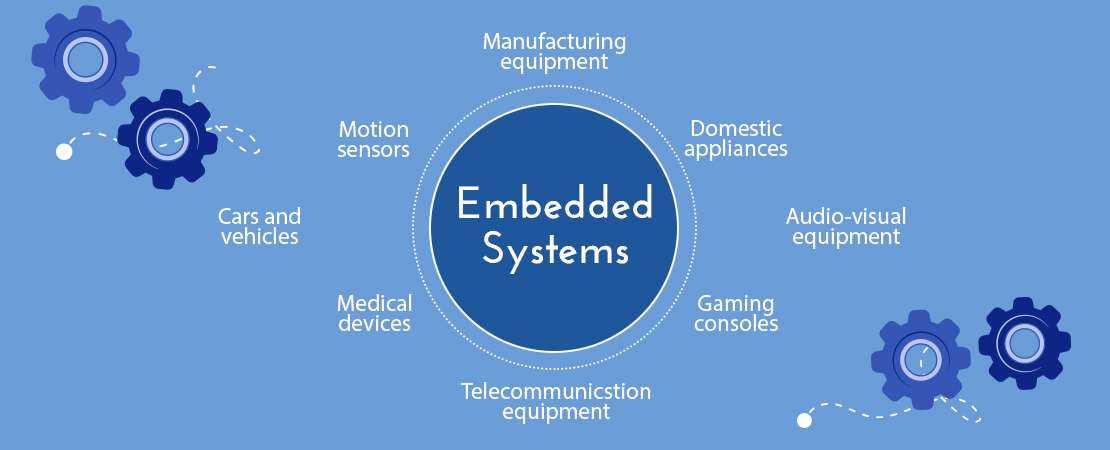
🔹 7. Applications
- Automotive systems (ECUs, ABS)
- Consumer electronics (TVs, washing machines)
- Medical devices
- Industrial control systems
- IoT devices
- Aerospace and defense systems
🔹 8. Challenges
- Limited memory and power
- Real-time constraints
- Hardware-software co-design
- Debugging and testing complexity
- Security and reliability
Conclusion
In conclusion, an embedded systems development architect for low-power medical devices does more than write code or design circuits; their job is to create sustainable, dependable, and trustworthy technology that enhances patient outcomes through careful engineering and adherence to regulations.